Threats in cybersecurity continue to evolve at exponential rates alongside the rapid advancement of technology, which calls for staying on top of the latest cybersecurity trends. As new technological developments are implemented, criminals come up with increasingly sophisticated and adaptive threats that pose significant challenges to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide.
Financial losses resulting from cyber crimes are also rising and are projected to grow from a global cost of $9.22 trillion in 2024 to $13.82 trillion by 2028. Although new and evolving cyber threats cannot be accurately predicted, it’s crucial to be aware of current trends, particularly for organizations.

The Latest Cybersecurity Trends
Throughout 2026, several emerging trends resulting from advancing technology and societal shifts are expected to reshape the cybersecurity industry and be addressed by professional cybersecurity services.
Adoption of AI Technology
The implications of AI advancement remain uncertain. While there is proven potential to use AI to defend against cyber threats, cyber criminals themselves are harnessing AI capabilities to engineer more sophisticated and dangerous attacks.
AI for cybersecurity has already been implemented by large organizations such as Google through defense initiatives to allow “security professionals and defenders to scale their work in threat detection, malware analysis, vulnerability detection, vulnerability fixing, and incident response.”
As this technology becomes increasingly accessible, even smaller businesses operating within tight security budgets will feasibly incorporate AI into their threat detection and response strategies.
However, the widespread adoption of AI also amplifies cybercriminals’ capabilities, which poses unique challenges to defenders, particularly businesses. AI algorithms allow criminals to automate various stages of their attack, including the selection of targets and evasion of detection systems, enabling them to operate at a much larger scale. In some cases, attackers pushed AI’s agentic capabilities further than ever before, using it to actively execute cyberattacks rather than act just as an advisor.
The increased availability of “off-the-shelf” AI-powered cybercrime tools and services in underground markets makes it easier for novice hackers to launch cyber attacks without the need for specialized technical skills or any significant resources.
Overall, while AI has become a key tool for protecting against cyber attacks, its accessibility has led to a tug-of-war between attackers and defenders. Both businesses and individuals must consider layering their defenses and facilitating open communication to win the AI threat standoff and successfully counter escalating cyber threats.
The Risks of Remote Working
During the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses worldwide began implementing work-from-home policies. In the following years, many employees were reluctant to return to their offices, leading to a steady increase in hybrid and remote working arrangements.
Despite remote working providing both businesses and employees a range of benefits, such as increased productivity, greater work-life balance, and reduced expenses, this new approach poses various cybersecurity risks. The average employee is unaware of prevalent cyber threats and may inadvertently engage in risky behaviors that could compromise their organization’s security.
For example, employees may fail to update their operating systems and software applications regularly, which could expose them to security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. If an employee chooses to work in a public location, such as a library or cafe, they could connect to an unsecured public Wi-Fi network, allowing criminals to intercept their data or remotely launch an attack on their device.
As remote working significantly expands an organization’s attack surface, the effectiveness of traditional security measures is reduced. Unlike in office spaces, security teams cannot monitor employees or enforce security policies in remote working environments.
Incident response times are also slower, which can allow cyber attacks to cause more severe and widespread damage to an organization before they are contained.
The Increasing Sophistication of Cyber Attacks
From ransomware and extortionware to deepfakes and phishing scams, 2024 and its surrounding years encompass a time when digital threats are evolving and advancing at an unprecedented rate.
Limitations of Traditional Cybersecurity Measures
During recent years, the prevalence and sophistication of cyber attacks have constantly increased. The steady rise of these threats has highlighted the inadequacy of conventional cybersecurity protocols in addressing, preventing, and managing them.
Traditionally, both physical and cyber defenses have focused on protecting against threats that originate outside an organization’s perimeter. However, this approach is less effective in the current digital threat landscape, as cyber-attacks are increasingly originating internally.
Social engineering attacks, compromised credentials, and employee negligence can cost an average of $17.4 million annually. Even with reactive measures, many organizations fail to respond promptly to these threats, resulting in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Cyberthreats have reached a level of sophistication where they can exploit software vulnerabilities, extract data, induce system downtime, and disrupt business operations within minutes, showcasing the limitations of traditional defenses.
Consequently, there’s increased pressure on businesses to embrace proactive security measures that prioritize preventing internal infiltration rather than solely reacting to incidents and spending extensive resources mitigating the resulting damage.
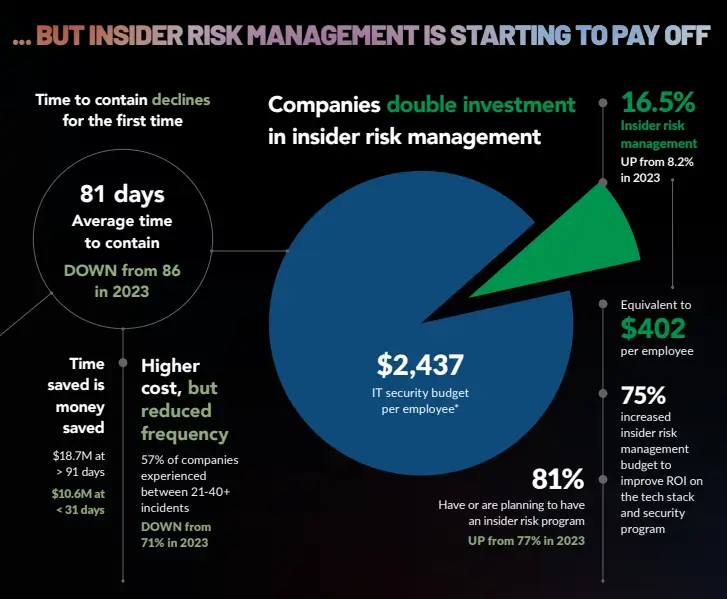
Rise of Ransomware
Ransomware, which employs encryption to hold a victim’s sensitive information and critical data ransom, is predicted to be the top cyber threat from 2024 onwards. Ransomware occurs in various forms and is often distributed through phishing emails or exploited software vulnerabilities.
Prior to 2016, ransomware attacks were rarely targeted and often relied on a ‘spray-and-pray’ technique, prioritizing attempts to reach as many victims as possible rather than focusing on a few specific targets. However, as ransomware attacks advanced, targeted approaches became more common, and criminals began laying more pressure on victims. As a result, the cost of ransomware skyrocketed, with average ransom payment costs growing from less than $6,000 to almost $240,000 between 2018 and 2020.
In the years leading up to 2026, ransomware has continued to evolve and experience exponential growth, threatening organizations of all sizes and industries. New forms of ransomware have also emerged, including “extortionware,” where attackers infiltrate a company’s digital resources and threaten to release them publicly unless a ransom is paid.
While larger organizations may have adequate resources to invest in their cybersecurity budget to prevent ransomware, smaller businesses are much more vulnerable. However, several steps can be taken to protect against attacks and mitigate the damage of ransomware, including:
- Regularly backing up all sensitive data on separate networks;
- Ensuring that all company devices are updated with the latest anti-virus software and firewalls;
- Keeping all on-premise company hardware up-to-date;
- Urging employees to use strong passwords and not repeat passwords on different accounts;
- Educating employees on best practices regarding clicking on links or sharing sensitive company information;
- Investing in cyber insurance to reduce the financial impact of a successful attack.
The FBI recommends organizations contact their nearest FBI field office or report the attack at tips.fbi.gov if they have been knowingly targeted by ransomware.
The Rising Risk of Deepfake Scams
Deepfake scams are another rising trend powered by the advancement and misuse of technology. Deepfakes are a form of synthetic media that has been digitally manipulated to replicate an individual’s likeness. Deepfakes can depict images, videos, and live streams that mislead viewers into believing false information.
After first being coined in 2017, deepfakes initially captured interest due to their potential in entertainment and digital art creation. However, as the technology advanced and became more accessible, malicious actors began using it to their advantage, leading to the growth of deepfake scams.
Deepfakes can impersonate celebrities, authority figures, and trusted individuals, such as government officials, through carefully curated video and audio. Scammers can simulate these targets endorsing products, requesting funds, or ordering others to engage in illegal activities. There are numerous examples of victims handing over sensitive information or sending large sums of money to a scammer, falsely believing they are interacting with the genuine person depicted in the deepfake.
Moving into 2026, deepfake scams continue to threaten businesses, leading to substantial losses stemming from employee deception. For instance, using AI website builders, scammers can create professional phishing sites in minutes or clone existing sites to steal data and credentials from users, gain unauthorized access to accounts, or trick employees into revealing sensitive company information.
One of the fastest-growing threats in identity fraud is the use of synthetic identity documents. Criminals are leveraging AI to create realistic fake documents, like driver’s licenses or passports, that can slip past standard KYC checks.
Synthetic identity documents focus solely on falsified or AI-generated images of official documents, and fraudsters exploit these visuals to open accounts, move money, or bypass compliance systems, making detection much harder without advanced verification technology.
Along with the progression of AI and synthetic media technology, deepfakes will continue to become more convincing and harder to distinguish, posing significant threats to society.
While preventing malicious deepfake use remains a significant challenge for authorities, businesses can take several measures to protect their assets and employees from the dangers of deepfake scams. This includes providing educational programs to help employees identify the signs of deepfake scams and implementing verification processes, such as secret passphrases, to prevent the approval of unauthorized requests from fraudulent sources.
The Future of Cybersecurity Trends
Several key cybersecurity trends have emerged in the years leading up to 2026 and will likely continue to impact the way organizations and individuals respond to and prevent digital threats.
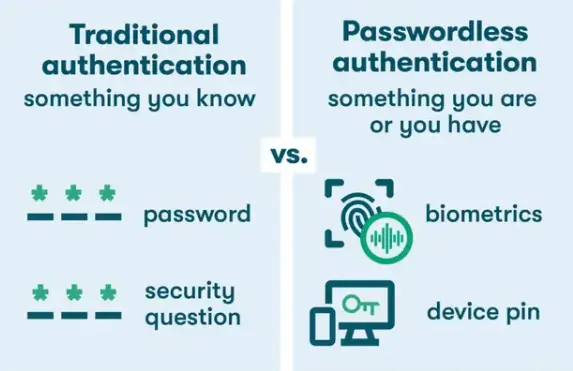
Adoption of Passwordless Authentication
In recent years, the inherent weaknesses of traditional passwords have become evident. The most noteworthy critical flaws of passwords include:
- Brute-force attacks: A common and easy-to-execute attack, known as a brute-force attack, involves a criminal repeatedly attempting to guess a victim’s password until they find the correct one.
- Security breaches: During security breaches, user passwords can be stolen and sold on the dark web, along with other sensitive credentials, in some cases, without the owner’s awareness.
- Password reuse: Password fatigue has become widespread, and many online users reuse passwords, which can risk all of an individual’s accounts if a single one is compromised.
- Keylogging malware: Keyloggers are a form of malware that records keystrokes as they’re typed by a victim. Through keylogging, attackers can identify a victim’s password and subsequently gain access to their accounts.
- Outsider observation: Particularly for remote workers, there is a high risk of their passwords being observed or recorded by an unauthorized individual who is surveilling them.
Passwords leave businesses and individuals susceptible to security breaches, so passwordless alternatives are steadily being adopted. Popular forms of passwordless authentication include biometrics, temporary security tokens, time-based links, and smart cards.
Through passwordless authentication, businesses can significantly reduce their attack surface while ensuring an enhanced user experience for employees. On a long-term basis, this will reduce costs associated with breached accounts and facilitate a faster login experience within amplified security.
Protection Against Human Error
Research has shown that the majority of cybersecurity issues can be traced back to human error. Although education and training surrounding cyber threats are gradually growing, organizations are urged to dedicate more resources to protect against attacks that rely on human error and reduce their resulting impact.
Phishing is a common social engineering attack in which criminals deceive victims into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and banking details. Attackers masquerade as reputable sources and use various tactics to trick individuals into providing this information or clicking on malicious links that infect their devices with malware.
Phishing scams are often targeted through messages, texts, phone calls, and emails, but can also be in the form of illegitimate websites. In the second quarter of 2025, over 1.1 million unique phishing attacks were observed by the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG).
It’s evident that phishing attacks are already commonplace and will continue to threaten organizations, potentially becoming more advanced and difficult to detect in the future. Therefore, the optimal course of action for organizations is to prioritize training their employees to recognize and report phishing attempts.
Phishing simulations can replicate real-world phishing scenarios within a controlled environment. They enable organizations to identify areas for improvement by assessing their employees’ susceptibility to phishing attacks. Regularly conducting these simulations will ensure employees remain vigilant and are well-informed on how to respond effectively to real-life phishing attacks.
Organizations must also focus on training all employees rather than those in specific departments, as phishing attacks can target individuals across any level. By promoting awareness of phishing and other social engineering attacks, organizations can establish a robust defense against these threats and provide greater protection against human error.
Cybersecurity Challenges
Despite an optimistic future, businesses have several future challenges to overcome regarding cybersecurity. With an increased reliance on cybersecurity professionals and the threat of external vulnerabilities, the progress businesses make toward subduing prevalent cyber threats may be stalled.
Professional Skill Gaps
According to an ISC2 Cybersecurity Workforce Study, economic pressures and budget constraints have slowed hiring and limited investment in skill development but have also created gaps in knowledge and competencies within organizations and their cybersecurity teams. This leaves teams less prepared to handle evolving threats and increases the risk of critical skill shortages.
As a result, there is now an exceptionally high demand for cybersecurity professionals across all industries. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects cybersecurity job openings to increase by 32% over the next decade, significantly outpacing the average growth rate for all occupations.
However, there is growing concern about an aging cybersecurity workforce. A 2025 report by ISACA suggests that as experienced cybersecurity professionals near retirement, there may not be enough talent with managerial experience to replace them, creating potential gaps in leadership and expertise.
If businesses cannot fill their cybersecurity positions, they will be unable to protect data and assets from advancing cyber threats. Consequently, there is heightened pressure to offer benefits to their cybersecurity and IT teams to ensure their retention and attract new recruits.
For businesses to recruit and retain cybersecurity employees, they must prioritize work-life balance and invest additional resources to support them. This can include facilitating flexible working hours, offering training opportunities, providing highly competitive compensation packages, and promoting a supportive work culture.
As employees feel valued and empowered in their roles, their performance will increase, further strengthening the organization’s defense against cyber attacks.
Third-Party Security Risks
While an organization may have a robust cybersecurity defense system in place, third parties, including vendors, suppliers, and contractors, might not adhere to the same standards. This can present additional risks for organizations, as third parties have access to their systems, data, and networks, which attackers can exploit.
When a third party experiences a security breach, organizations are forced to respond and attempt to mitigate risks outside their defense infrastructure to protect their assets and reputations. Despite these concerns, most organizations fail to delegate adequate resources to manage third-party security risks.
To effectively manage these risks, organizations must keep an updated vendor inventory and carefully assess new vendors to track and manage their fluctuating attack surface. These processes can incur additional costs that many organizations did not initially account for, resulting in exceeded cybersecurity budgets.
However, with research suggesting that most data breaches can be linked back to third-party vendors, focusing on establishing robust vendor management practices is imperative.
Conclusion
In 2026, we can expect to see the rise and development of various trends in the cybersecurity space. New shifts in technology, developments of threats, and adjustments of priorities present various challenges for society. Notably, organizations are pressured to respond to emerging threats and implement scalable solutions without exceeding their security budgets.
By analyzing current and predicted trends, organizations can adopt proactive and innovative cyber threat defense measures to protect their assets and remain ahead of the curve of advancing cybersecurity risks.
If you need a deeper understanding of current cybersecurity trends and ways to safeguard your business, contact American Security Force to get expert support.



